Java - DES Encryption and Decryption example
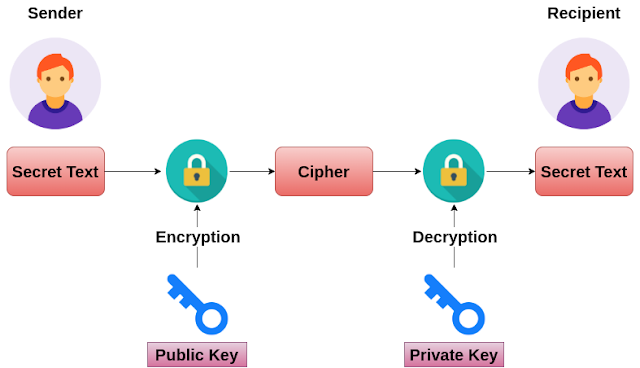
DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm is the most commonly used encryption symmetric-key algorithm in the world. For a long time, "cipher generation" was synonymous with DES in many people's minds. Although the Electronic Frontier Foundation recently called, it built a 220,000 machine to try to crack DES encrypted data. DES and its variant "triple data encryption algorithm" will still be widely used in government and banking. AES became the replacement for DES). DES processes bits or binary numbers. We know that every four bits make up a hexadecimal number. DES encrypts a set of 64-bit information, which is represented by 16 hexadecimal numbers. DES also uses 64-bit long ciphers to provide encryption. However, every 8 bits in the key are ignored, resulting in a correct key length of 56 bits in DES. However, in any case, one 64-bit block is an eternal DES organization. Java DES Encryption and Decryption import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.K