Azure DevOps - CI/CD pipeline for container-based system
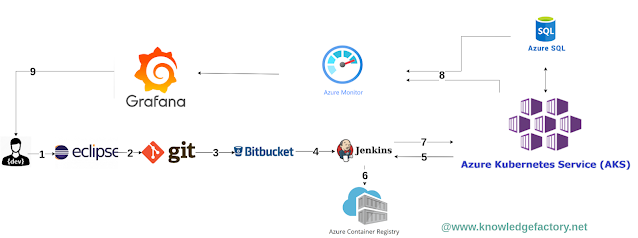
Azure provides a set of flexible services designed to enable companies to more rapidly and reliably build and deliver products using Containers and DevOps practices. These services simplify provisioning and managing infrastructure, deploying application code, automating software release processes, and monitoring your application and infrastructure performance. In this post, we will learn how to modernize spring web application development by using containers and DevOps workflows. In this example, A Spring web app is built and deployed by Jenkins into an Azure Container Registry and Azure Kubernetes service. For a globally distributed database tier, Azure SQL Database is utilized. To monitor and troubleshoot application performance, Azure Monitor integrates with a Grafana instance and dashboard. Today modern application development uses continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD), we can more expeditiously build, test, and deploy services. This modern approach lets us rel