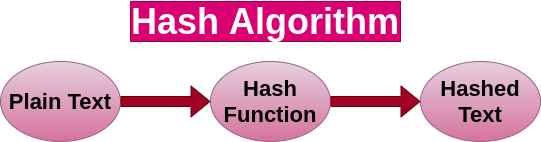
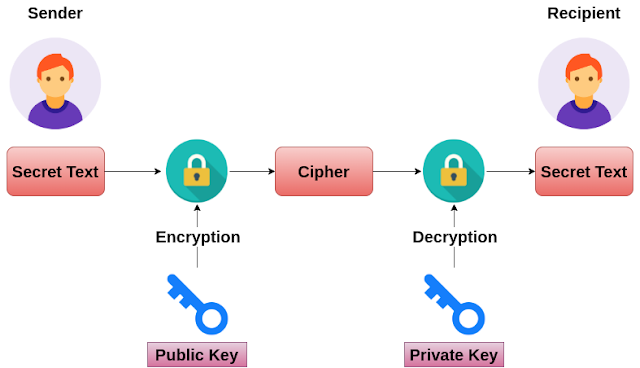
Go Language - Maps - Example
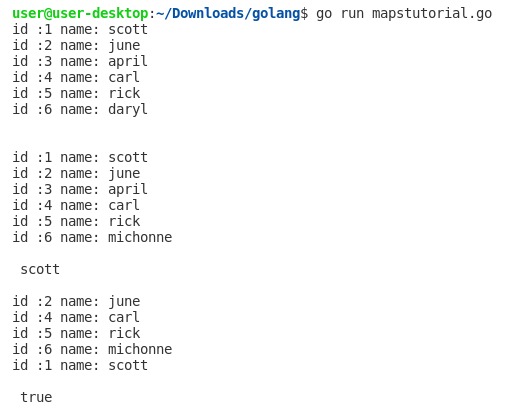
A map is an unordered collection of key/value pairs, where each key is unique. We can create a new map with a make statement or a map literal. The default zero value of a map is nil. The len function returns the size of a map. Go Range keyword is used in different kinds of data structures in order to iterate over elements. Create a Map: Create a Map called users that will store int keys and String values: /* Create a new map * Empty map of string-string pairs */ users := make( map [ int ] string ) Add Items: Add a new key-value pair, //Add Items users[ 1 ] = "scott" users[ 2 ] = "june" users[ 3 ] = "april" users[ 4 ] = "carl" users[ 5 ] = "rick" users[ 6 ] = "daryl" Update Value: // Update value users[ 6 ] = "michonne" Iterate over all keys and values: // Iterating over all keys and values for id, name := range users { fmt.Printf( "id :%d name: