Spring Boot - Testing a Data MongoDB application with Testcontainers and @DataMongoTest
In this section, we will learn how to test Repository layer components with @DataMongoTest and Testcontainers in Spring Boot Data MongoDB application that uses MongoDB as database.
1. What we will build?
We will create a basic Data MongoDB Spring Boot application that uses MongoDB as database. We will create Repository layer for this application. Finally we will do a testing with help of Testcontainers and @DataMongoTest to verify our system is working as expected.
2. Testcontainers
Testcontainers is an open source testing library that allows us to run docker containers directly in our spring boot application in order to facilitate integration tests with real dependencies.
It can provide instances of common databases(here MongoDB), message brokers, Selenium web browsers, or anything else that can run in a Docker container.
3. @DataMongoTest
Instead of bootstrapping the entire application context for every test, @DataMongoTest allows us to initialize the Spring application context with only those beans needed to test Data MongoDB-based components.
By default, it scans for @Document classes and configures Spring Data MongoDB repositories. It will auto-configure MongoTemplate. If an embedded database is available on the classpath, @DataMongoTest will autoconfigure one for testing purposes.
Do you want more information about @DataMongoTest? Click here
4. Install docker
Install docker in your local machine if you not yet installed docker. Go to docker official https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/#desktop and download docker and then install.
5. Creating a spring boot application
First, open the Spring initializr https://start.spring.io
Then, Provide the Group and Artifact name. We have provided Group name com.knf.dev.demo and Artifact datamongotest-testcontainers-testing-example. Here I selected the Maven project - language Java 17 - Spring Boot 3.1.6, Testcontainers, and Spring Data MongoDB.
Then, click on the Generate button. When we click on the Generate button, it starts packing the project in a .zip(datamongotest-testcontainers-testing-example) file and downloads the project. Then, Extract the Zip file.
Then, import the project on your favourite IDE.
Final Project directory:
Complete pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.knf.dev.demo</groupId>
<artifactId>datamongotest-testcontainers-testing-example</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>datamongotest-testcontainers-testing-example</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-testcontainers</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testcontainers</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testcontainers</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<image>
<builder>paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest</builder>
</image>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
spring-boot-testcontainers:By using this dependency spring automatically configures the necessary Spring Boot properties for the supporting containers.
junit-jupiter testcontainers extension which will take care of starting and stopping of the containers.
spring-boot-starter-test starter will provide following libraries:
- JUnit
- Spring Test & Spring Boot Test
- AssertJ
- Hamcrest
- Mockito
- JSONassert
- JsonPath
Spring Data MongoDB– Student Document
package com.knf.dev.demo.document;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Document(collection = "students")
public class Student {
@Id
private String id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String id, String name, String email, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
- @Document is used to map a class to mongoDB database, it represents a MongoDB documents.
Spring Data MongoDB– Student Repository
It doesn't make sense to test inherited default methods like save(), findById(), deleteById(), or findAll() from MongoRepository. If we are doing like so, means we are testing the framework.
So, i created three methods findByName() , findByAgeGreaterThan() , and findByAgeLessThan().
package com.knf.dev.demo.repository;
import com.knf.dev.demo.document.Student;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Query;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface StudentRepository extends MongoRepository<Student, String> {
@Query("{name : ?0}")
Optional<Student> findByName(String name);
@Query("{ age : { $gte: ?0 } }")
List<Student> findByAgeGreaterThan(Integer age);
//Derived Query Method
List<Student> findByAgeLessThan(Integer age);
}
- findByAgeGreaterThan(): If we want to retrieve students whose age is greater than the given age.
- findByName(): This method will get student entity by name.
- findByAgeLessThan(): If we want to retrieve students whose age is less than the given age.
- MongoRepository provides all the necessary methods which help to create a CRUD application and it also supports the custom derived query methods.
Application.java
package com.knf.dev.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
Implementing the Tests
When using JUnit 4, this annotation should be used in combination with @RunWith(SpringRunner.class). But for this example we are using JUnit 5, there’s no need to add the equivalent @ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class).
package com.knf.dev.demo;
import com.knf.dev.demo.document.Student;
import com.knf.dev.demo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.data.mongo.DataMongoTest;
import org.springframework.boot.testcontainers.service.connection.ServiceConnection;
import org.testcontainers.containers.MongoDBContainer;
import org.testcontainers.junit.jupiter.Container;
import org.testcontainers.junit.jupiter.Testcontainers;
import org.testcontainers.utility.DockerImageName;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import static org.assertj.core.api.AssertionsForInterfaceTypes.assertThat;
@DataMongoTest
@Testcontainers
public class StudentRepositoryTest {
// @Autowired
//private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Container
@ServiceConnection
public static MongoDBContainer mongoDBContainer =
new MongoDBContainer(DockerImageName.parse("mongo:latest"));
//Method should be executed before all tests in the current test class
//Load initial data
@BeforeAll
static void setup(@Autowired StudentRepository studentRepository) {
Student student1 = new Student("101","Alpha","alpha@knf.com",50);
Student student2 = new Student("102","Beta","beta@knf.com",40);
Student student3 = new Student("103","Gama","gama@knf.com",30);
Student student4 = new Student("104","Pekka","pekka@knf.com",20);
List<Student> students = Arrays.asList(student1,student2,student3,student4);
studentRepository.saveAll(students);
}
@Test
void findByName_ReturnsTheStudent() {
Student student = studentRepository.findByName("Alpha").get();
assertThat(student).isNotNull();
assertThat(student.getEmail()).isEqualTo("alpha@knf.com");
assertThat(student.getName()).isEqualTo("Alpha");
assertThat(student.getId()).isEqualTo("101");
assertThat(student.getAge()).isEqualTo(50);
}
@Test
void findByAgeGreaterThan_ReturnsTheListStudents() {
List<Student> students = studentRepository.findByAgeGreaterThan(29);
//Convert list of students to list of id(String)
List<String> ids = students.stream()
.map(o -> o.getId())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertThat(students.size()).isEqualTo(3);
assertThat(ids).hasSameElementsAs(Arrays.asList("103","102","101"));
}
@Test
void findByAgeLessThan_ReturnsTheListStudents() {
List<Student> students = studentRepository.findByAgeLessThan(31);
//Convert list of students to list of id(Integer)
List<String> ids = students.stream()
.map(o -> o.getId())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
assertThat(students.size()).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(ids).hasSameElementsAs(Arrays.asList("104","103"));
}
}
- @Testcontainers is a JUnit Jupiter extension which automatically starts and stops the containers(here MongoDBContainer) that are used in the tests.
- The @Container annotation is a JUnit extension that tells JUnit to notify this field about various events in a test lifecycle. In this case, it ensures that the MongoDB container is running in a healthy way before any test is considered successfully run.
- Beginning from Spring Boot version 3.1, the annotation @ServiceConnection can be used on the container instance fields of our tests. We are using @ServiceConnection instead of @DynamicPropertySource to register the dynamic property values to a MongoDB container.
- Testcontainers has a MongoDBContainer class that enables you to create a MongoDB instance for testing purposes.
- assertThat is used to check the specified value matches the expected value. It will accept the two parameters, the first contains the actual value, and the second will have the object matching the condition.
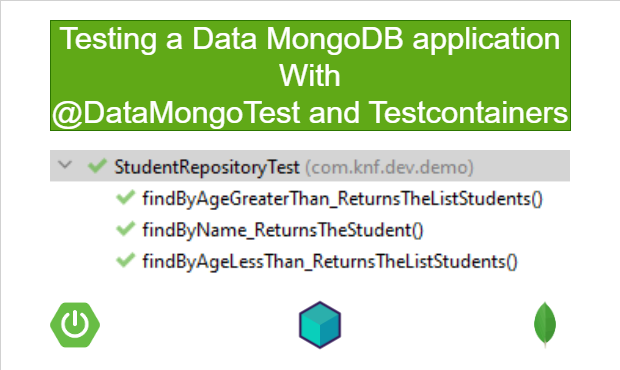
6. Run the test
Since we are using Testcontainers, make sure to start Docker in your local machine.
After that, run the test,
Or you can run the test using following command:
mvn test -Dtest=StudentRepositoryTest
ormvn test